Questions
7
Answers
7
-
Asked on 24 2 月, 2025 in FAQ.
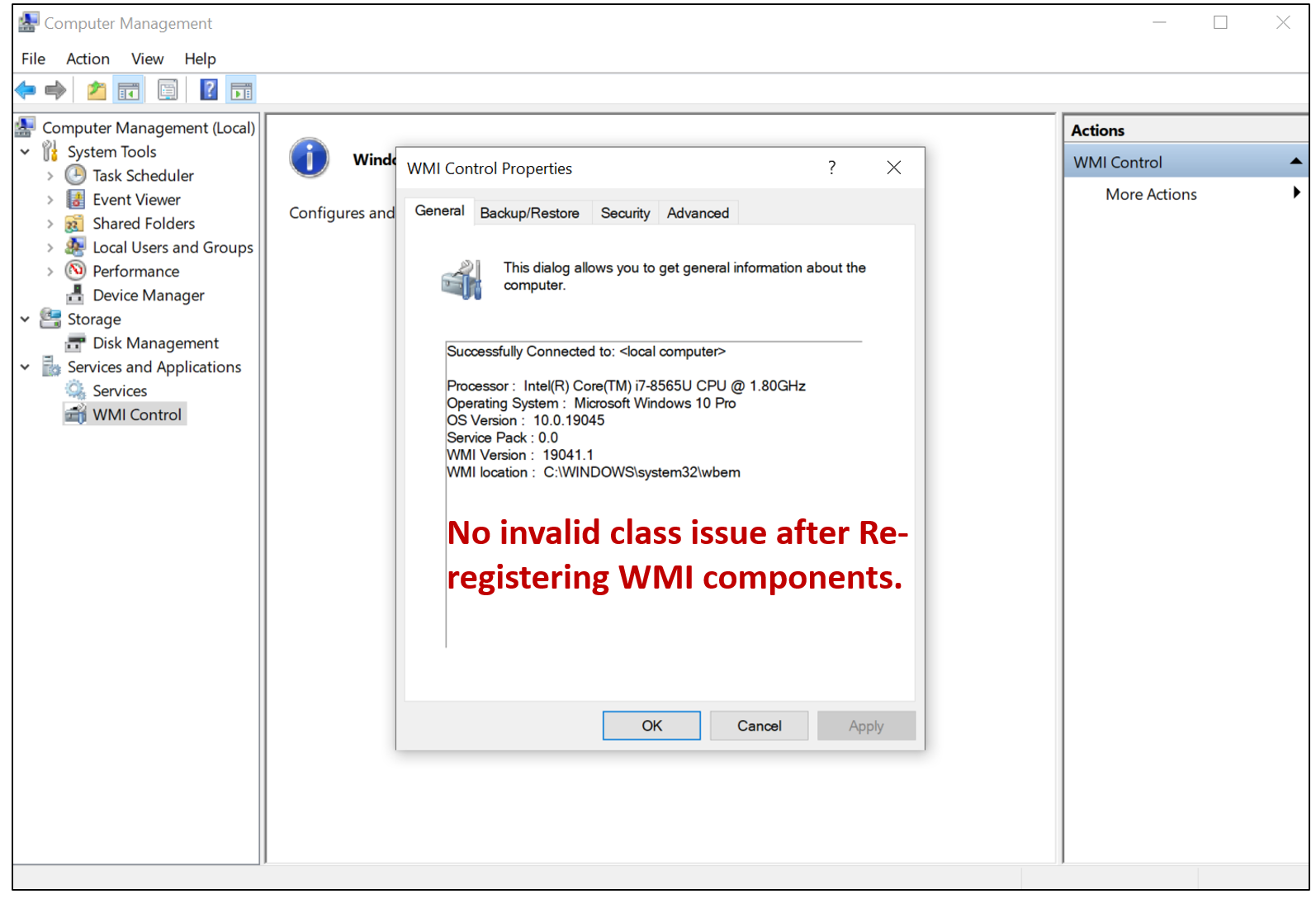
Step 1. Confirm if there is WMI Invalid class issue on the computer
- Press the ‘Win + R’ keyboard shortcut
- Type ‘compmgmt.msc‘ in the blank field
- Press the ‘Ok’ button
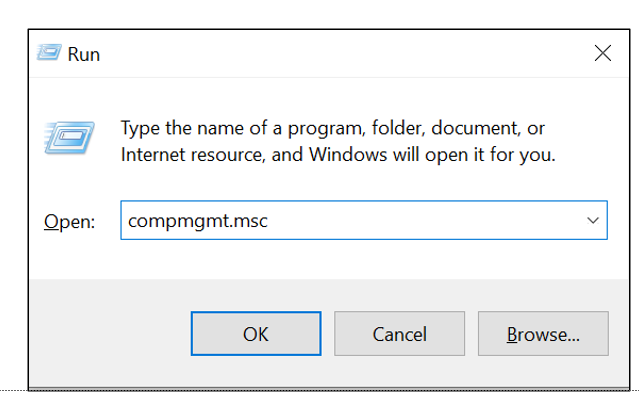
- Right-click on WMI Control and select ‘Properties.’
- Check if the computer has any WMI invalid class issues
Step 2. Re-registering WMI components
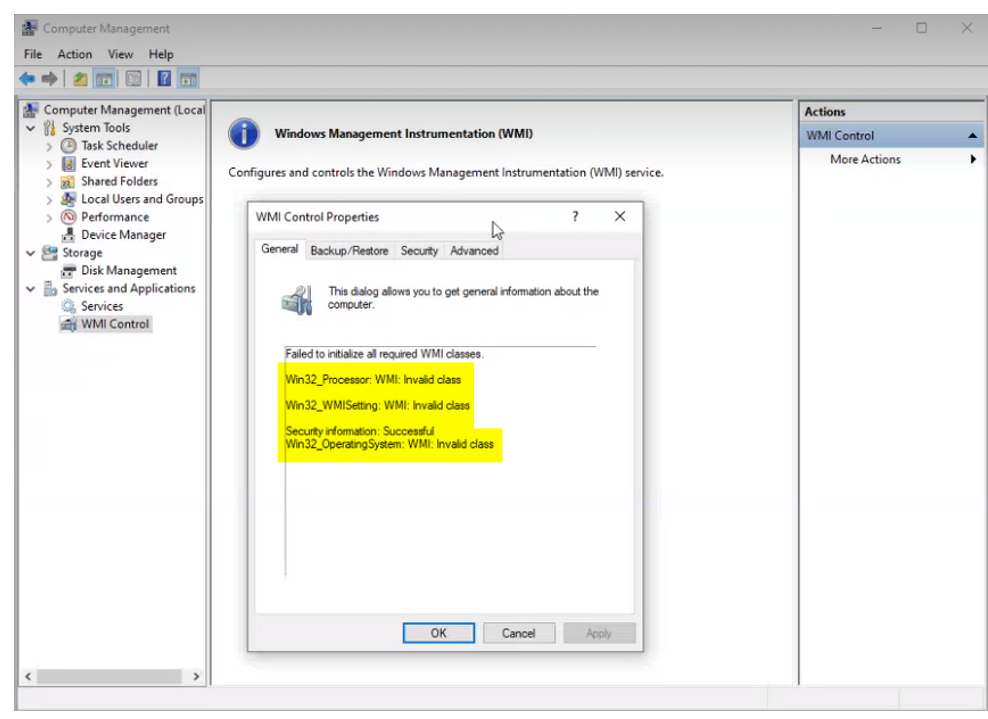
- The .DLL and .EXE files used by WMI are located in %windir%\system32\wbem. You might need to re-register all the .DLL and .EXE files in this directory. If you are running a 64-bit system you might also need to check for .DLLS and .EXE files in %windir%\sysWOW64\wem
- Open Command Prompt as administrator.
- To re-register the WMI components, run the following commands at the command prompt (Enter a command and press Enter. Wait for it to finish, and then input the next one.):
Step 3. Go to WMI to see if the invalid class issue is fixed
Reference:
- 496 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 23 12 月, 2024 in Moldex3D.
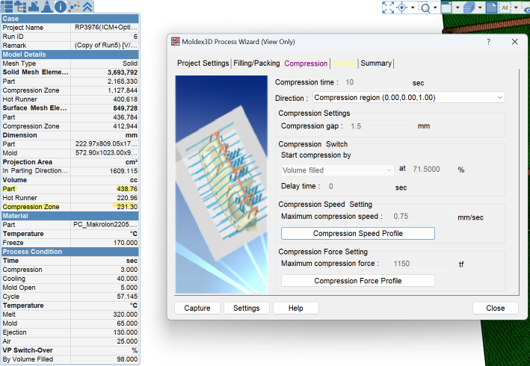
This means that before the compression switch, the amount of resin injected is calculated as: (Part + Compression) * VP switched volume (i.e., 70%).
Therefore, the difference in resin volume is an influencing factor that causes the variation in warpage. The change in resin quantity affects the pressure, which in turn influences warpage.
.
- 685 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 23 12 月, 2024 in Moldex3D.
- 612 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
Asked on 11 11 月, 2024 in FAQ.
- 548 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
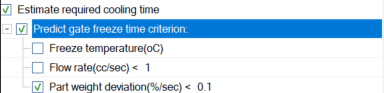
Asked on 11 11 月, 2024 in FAQ.The factors considered in Moldex3D’s AutoHTC include:1. Part:
-
Part thickness
2. Plastic Material:-
Density
-
Specific heat capacity (Cp)
-
Thermal conductivity (K)
3. Mold Material:-
Density
-
Specific heat capacity (Cp)
-
Thermal conductivity (K)
4. Process Conditions:-
Mold temperature
-
Melt temperature
-
Filling time
This answer accepted by Jessie. on 3 2 月, 2026 Earned 0 points.
- 595 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
-
Asked on 23 9 月, 2024 in FAQ.Warpage Results vs. Differential Shrinkage EffectOur warpage solver primarily considers two main effects: differential temperature and differential shrinkage effects.Differential shrinkage effects The differential shrinkage displacement represents the in-plane shrinkage due to PVT distribution. The displacement is calculated based on the average volumetric shrinkage across the thickness of the same cutting plane. Since this effect averages across the thickness, it does not vary in the vertical (thickness) direction.On the other hand, Differential temperature effect displacement is calculated with the difference of volumetric shrinkage through thickness. it represents the out-of-plane warpage.
- 534 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes
-
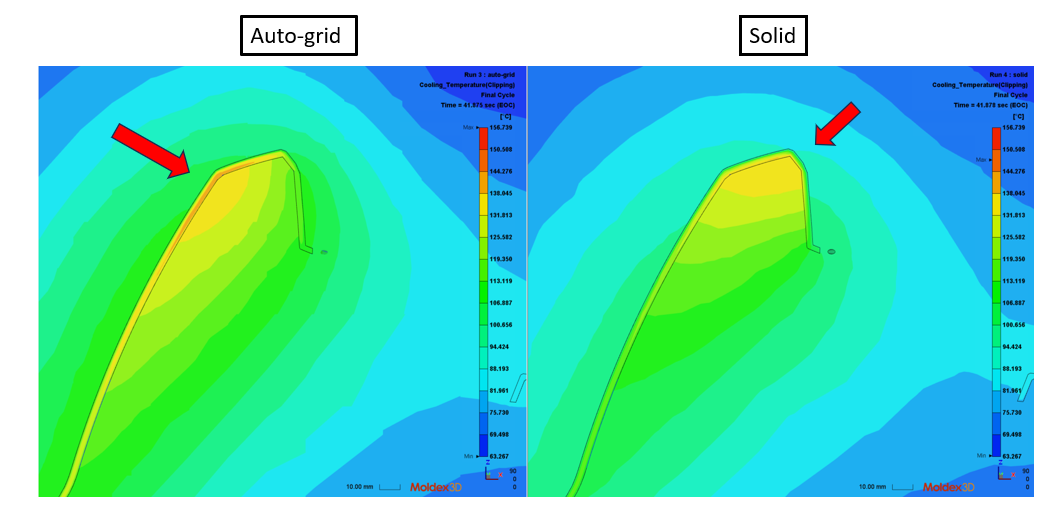
Asked on 23 9 月, 2024 in FAQ.Basically, Fast Cool(auto-grid mesh) and Standard Cool(solid mesh) have similar results. However, in some cases, especially for complex and thick parts, the results may differ.For example, in this case, the heat accumulation occurs in different area.To avoid this kind of situations and achieve more precise results, we recommend using standard cool(with solid mesh) for the analysis.
- 512 views
- 1 answers
- 0 votes